
Hello
Select Address
With the growing need for enteral nutrition in the U.S, enteral knowledge is mandatory. Proper nutrition is what makes a person healthy and gives them the ability to recuperate. When a person is getting nutrition solely through enteral feeding, the caregiver, as well as the family members, should have the right knowledge of the patient’s nutritional needs, enteral procedure and complications, and various enteral feeding accessories.
Here is a list of essential Enteral Feeding Accessories
1. Gastrostomy Feeding Tube
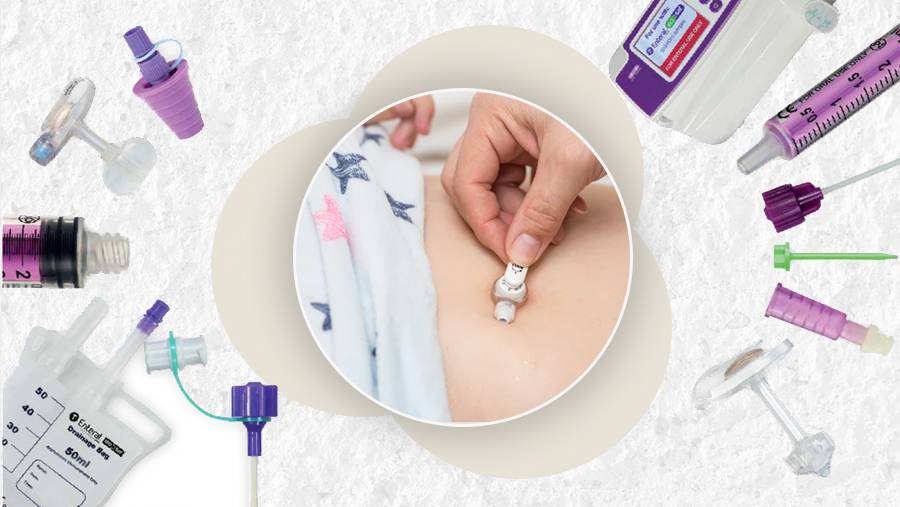
A gastrostomy feeding tube also called a G-tube is a device inserted through the abdominal area directly into the stomach for nutrition.
G-tube is needed by individuals with different kinds of health problems – inherent disorders of the mouth, esophagus, stomach or intestine; swallowing incapability or insufficiency of nutrition.
A gastrostomy tube is inserted through a combination of methods – a laparoscopic technique for two small incisions; open surgery for large incision or a PEG procedure with some body-fluid drainage like blood or pus may occur from the wound.
2. Jejunostomy Feeding Tube
A jejunostomy feeding tube is like a G-tube inserted into the middle section of the intestine. It is instead called a J-tube. J-tube tubes are generally used less when compared to G-tubes. These are suggested when it is impossible to place a gastrostomy tube for anatomical reasons. There are varied ways of J-tube placement – endoscopic placement or laparoscopic surgery. A surgeon creates an incision in the abdomen and makes a small opening called a jejunum. Dressing is used to keep the tube in place.
3. Nasogastric Feeding Tube
A nasogastric feeding tube is a device that goes through the nose directly into the stomach. Nasogastric feeding is generally used for infants who cannot intake enough nutrition and children who find difficulty in eating through the mouth. Pediatric nutrition such as breast milk, formula or liquid food is provided through this tube to give the child extra nutrition. Adults can also opt for nasal tubing to avoid surgical procedures.
Nasogastric tubing is a non-surgical method of placing the tube into the stomach. The distance between the child’s nose to the esophagus is first measured and the tube is cut accordingly and then the tubing is placed.
4. Enteral Feeding Pump
An enteral feeding pump is an electronic device that controls the feed flow delivered to a patient. The pump administers a measured amount of nutrition through a span of 24 hours – continuous or periodic.
Enteral Feeding pumps are precise in measurement and timing, but it is just a machine that presumably can malfunction, resulting in the delivery of too much or too little nutrition.
The latest pumps in the market come with numerous safety measures with an error indication and backup mechanism to make failures unlikely.
5. Safety Screw Spike
A safety screw spike is configured to connect the enteral feeding bottle or pouch to the enteral feeding pump. A screw spike's objective is to connect every part of the enteral feeding system properly to avoid device misalliance and provide a secure fit.
A safety screw spike is a single patient use, so there is no chance of cross-contamination of any kind.
6. Enteral Feeding Valve
Enteral Feeding valves are non-sterile, latex-free components with a tethered cap structure. A valve allows the administration of nutrition and medication through a faucet technology using a syringe without having to disconnect the feeding line. These prove beneficial as it reduces the exposure of medical workers to certain infectious body fluids and bloodborne pathogenic secretions. These valves also reduce enteral tubing failures.
7. Enteral Declogger
Tube blockage is easier prevented than corrected. When a patient’s feeding tube gets clogged, are you going to replace it with a new tubing? Well, that is expensive. A de-clogger is a plaint and threaded device that drills through the blockage and restores the nutrition and medication passageway.
A de-clogger cannot be reused and is totally safe as it comes with molded safeguards to prevent over-insertion.
8. Enteral Decompression Tube
Decompressors are used for symbolic patients with inoperative and malevolent bowel obstruction. Bowel obstruction is a very common occurrence in patients with cancer. Placing a post-pyloric decompressor through the gastrostomy reduces bowel obstruction.
Enteral feeding for acquiring nutrition is a very common medical support in the United States. Hope this blog provides enough knowledge regarding enteral feeding accessories.